$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 1.&\textrm{Daerah yang diarsir berikut adalah himpunan}\\ &\textrm{penyelesaian pertidaksamaan dari}....\\ \end{array}$
Contoh Soal 1 Program Linear (Matematika Wajib Kelas XI)
Program Linear Dua Variabel (Matematika Wajib Kelas XI)
$\LARGE\color{blue}\textrm{A. Pendahuluan}$
Untuk menguasai materi ini, materi prasyarat yang harus pembaca kuasai adalah materi tentang persamaan linier dua variabel dan tentunya materi pertidaksamaan linear satu variabel. Materi program linear ini banyak digunakan dalam bidang ekonomi khususnya masalah optimasi.
$\LARGE\color{blue}\textrm{B. Sistem Pertidaksamaan Linear Dua Variabel}$
Sebelumnya perhatikanlah ilustrasi berikut
Bentuk umum yang akan digunakan dalam bahasan ini adalah sebagai berikut
$\color{blue}\begin{aligned}&\begin{cases} ax+by &\geq m \\ ax+by &>m \\ cx+dy &\leq n \\ cx+dy & <n \end{cases}\\\\ &\color{magenta}\textrm{dengan}\\ &a,b,c,d,m,n\: \: \textrm{bilangan riil}\\ &\color{magenta}\textrm{serta}\\ &x,y\: \: \textrm{keduanya adalah peubah bebas/variabel} \end{aligned}$
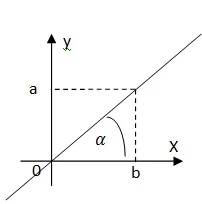
Sebagai misal
Untuk membantu menentukan pertidaksamaan linear dua variabel di atas tentunya penting juga membuat persamaan garis lurus (linear) sebagai prasyarat untuk membuat pertidaksaan yang dimaksud, yaitu:
$\begin{aligned}&\textrm{maka persamaan garisnya adalah}:\\ &(1)\qquad ax-by=0,\: \: \textrm{atau}\\ &(2)\qquad y=\left (\tan \alpha \right )x \end{aligned}$
dan jika garisnya berupa ilustrasi berikut
$\begin{aligned}&\textrm{maka persamaan gradien dan garisnya adalah}:\\ &(1)\qquad m=\displaystyle \frac{y_{2}-y_{1}}{x_{2}-x_{1}},\: \: \textrm{dan}\\ &(2)\qquad y=m\left ( x-x_{1} \right )+y_{1} \end{aligned}$
Dalam program linear terdapat dua hal yang harus diperhatikan yang berkaitan dalam penyelesaian dari masalah optimasi nantinya, yaitu kendala-kendala berupa pertidaksamaan linear dua variabel yang menjadi bahasan utama dan fungsi objektif sebagai fungsi sasarannya untuk mendapatkan dan menentukan mana yang nantinya dinyatakan suatu vektek (titik pojok) sebagai titik maksimum atau minimum.
$\LARGE\color{blue}\textrm{C. Nilai Optimum Fungsi Objektif}$
Bentuk umum dari fungsi objektif ini adalah
$\LARGE\color{magenta}\boxed{f(x,y)=ax+by}$
Fungsi optimum ini akan menunjukkan keoptimumnya mana kala titik-titik pojok disubstitusikan pada fungsi ini sehingga akan didapatkan nilai maksimum atau minimunya.
Untuk mendapatkan nilai optimum dari fungsi objektif ini dapat digunakan salah satu metode berikut
- metode uji titik pojok
- metode garis selidik
DAFTAR PUSTAKA
- Muis, A. 2009. Perang Siasat Matematika Dasar. Bantul: KREASI WACANA
- Tim VisiMath. 2009. 5000Plus Soal Matematika. Jakarta: Cerdas Interaktif
Contoh Soal 5 Induksi Matematika (Matematika Wajib Kelas XI)
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 21.&\textrm{Diketahui bahwa}\: \: S(n)\: \: \textrm{adalah formula dari}\\ &3+6+12+24+...+\left ( 3.2^{n-1} \right )=3.\left ( 2^{n}-1 \right )\\ &\textrm{Jika}\: \: S(n)\: \: \textrm{benar, untuk}\: \: n=k+1,\: \: \textrm{maka}\\ &\textrm{ruas kiri persamaan tersebut dapat dituliskan}\\ &\textrm{dengan}\: ....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&3+6+12+24+...+ 3.2^{k+1} \\ \textrm{b}.&3+6+12+24+...+ 3.2^{k-1} \\ \color{red}\textrm{c}.&3+6+12+24+...+ 3.2^{k-1}+3.2^{k} \\ \textrm{d}.&3+6+12+24+...+ 3.2^{k-1}+3.2^{k+1} \\ \textrm{e}.&3+6+12+24+...+ 3.2^{k}+3.2^{k+1} \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{c}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}&3+6+12+24+...+ 3.2^{n-1} =3.\left ( 2^{n}-1 \right )\\ &\color{red}3+6+12+24+...+ 3.2^{k-1}+3.2^{k}\color{black}=3.\left ( 2^{k+1}-1 \right ) \end{aligned} \end{array}$
DAFTAR PUSTAKA
- Budhi, W.S. 2018. Bupena Matematika SMA/MA Kelas XI Kelompok Wajib. Jakarta: ERLANGGA.
Contoh Soal 4 Induksi Matematika (Matematika Wajib Kelas XI)
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 16.&\textrm{Diketahui}\: \: 1+5+9+...+(4n-1)=2n^{2}-n\\ &\textrm{dengan}\: \: n\: \: \textrm{bilangan asli}.\: \textrm{Jika}\: \: m<k\: \: \textrm{dengan}\\ &m,k\: \: \textrm{bilangan asli juga},\: \textrm{maka}\\ &(4m-3)+(4m+1)+...+(4k-3)=....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&(k-m)(2k+2m-2)\\ \color{red}\textrm{b}.&(k-m+1)(2k+2m-3)\\ \textrm{c}.&(k-m+1)(2k-2m+1)\\ \textrm{d}.&(k-m+1)(2k^{2}+2m^{2}-3)\\ \textrm{e}.&(k-m)^{2}(2k-2m+4) \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{b}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}&1+5+9+...+(4m-3)+(4m+1)+...+(4k-3)\\ &=\underset{2k^{2}-k}{\underbrace{1+5+...+(4k-3)}}-\underset{2(m-1)^{2}-(m-1)}{\underbrace{1+5+...+(4(m-1)-3)}}\\ &=2k^{2}-k-\left ( 2(m-1)^{2}-(m-1) \right )\\ &=2k^{2}-k-2(m-1)^{2}+(m-1)\\ &=2k^{2}-k-2\left ( m^{2}-2m+1 \right )+m-1\\ &=2k^{2}-k-2m^{2}+4m-2+m-1\\ &=2k^{2}-k-2m^{2}+5m-3\\ &=(k-m+1)(2k+2m-3) \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 17.&\textrm{Diketahui}\: \: 2^{1}+2^{2}+2^{3}+...+2^{n}=2^{n+1}-2\\ &\textrm{dengan}\: \: n\: \: \textrm{bilangan asli}.\: \textrm{Jika}\: \: k\: \: \textrm{bilangan asli},\\ &\textrm{maka}\: \: 2^{2}+2^{3}+2^{4}+...+2^{k}+2^{k+1}=....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&(k-m)(2k+2m-2)\\ \textrm{b}.&(k-m+1)(2k+2m-3)\\ \textrm{c}.&(k-m+1)(2k-2m+1)\\ \color{red}\textrm{d}.&(k-m+1)(2k^{2}+2m^{2}-3)\\ \textrm{e}.&(k-m)^{2}(2k-2m+4) \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{d}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}&2^{2}+2^{3}+2^{4}+...+2^{k}+2^{k+1}\\ &=2^{1}+2^{2}+2^{3}+2^{4}+...+2^{k}+2^{k+1}-2^{1}\\ &=\underset{2^{k+1+1}-2}{\underbrace{2^{1}+2^{2}+2^{3}+2^{4}+...+2^{k}+2^{k+1}}}-2^{1}\\ &=2^{k+2}-2-2\\ &=2^{k+2}-4\\ &=2^{k}.2^{2}-4\\ &=2^{k}\times 4-4\\ &=4\left ( 2^{k}-1 \right ) \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 18.&\textrm{Diketahui bahwa}\: \: S(n)\: \: \textrm{adalah formula dari}\\ &2+5+10+17+...+\left ( n^{2}+1 \right )=\displaystyle \frac{1}{6}(n+1)\left ( 2n^{2}+n+6 \right )\\ &\textrm{Jika}\: \: S(n)\: \: \textrm{benar, untuk}\: \: n=k,\: \: \textrm{maka}....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \color{red}\textrm{a}.&2+5+10+17+...+\left ( k^{2}+1 \right )\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{1}{6}(k+1)\left ( 2k^{2}+k+6 \right )\\ \textrm{b}.&2+5+10+17+...+\left ( n^{2}+1 \right )\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{1}{6}(k+1)\left ( 2k^{2}+k+6 \right )\\ \textrm{c}.&2+5+10+17+...+\left ( k^{2}+2 \right )\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{1}{6}(k+2)\left ( 2k^{2}+5k+9 \right )\\ \textrm{d}.&\left ( k^{2}+1 \right )=\displaystyle \frac{1}{6}(k+1)\left ( 2k^{2}+k+6 \right )\\ \textrm{e}.&\left ( n^{2}+2 \right )=\displaystyle \frac{1}{6}(n+1)\left ( 2n^{2}+5n+9 \right ) \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{a}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}&\textrm{Cukup jelas}\\ &\textrm{Tinggal mensubstitusikan dari}\\ &\textrm{tiap}\: \: n\: \: \textrm{diganti}\: \: k \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 19.&\textrm{Diketahui bahwa}\: \: S(n)\: \: \textrm{adalah formula dari}\\ &12+17+22+...+\left ( 5n+7 \right )=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}(n+1)(5n+14)\\ &\textrm{Jika}\: \: S(n)\: \: \textrm{benar, untuk}\: \: n=k,\: \: \textrm{maka benar}\\ &\textrm{untuk}\: \: n=k+1.\: \textrm{Pernyataan ini dapat}\\ &\textrm{dinyatakan dengan}\: ....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&12+17+22+...+\left ( 5k+7 \right )=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}(k+1)(5k+14)\\ \textrm{b}.&12+17+22+...+\left ( 5k+7 \right )=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}(k+1)(5k+19)\\ \textrm{c}.&12+17+22+...+\left ( 5k+12 \right )=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}(k+1)(5k+19)\\ \textrm{d}.&12+17+22+...+\left ( 5k+12 \right )=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}(k+2)(5k+14)\\ \color{red}\textrm{e}.&12+17+22+...+\left ( 5k+12 \right )=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}(k+2)(5k+19) \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{e}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}&12+17+22+...+\left ( 5k+7 \right )=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}(k+1)(5k+14)\\ &12+17+22+...+\left ( 5(k+1)+7 \right )\\ &\qquad\qquad\qquad\quad=\displaystyle \color{magenta}\frac{1}{2}((k+1)+1)(5(k+1)+14)\\ &12+17+22+...+\left ( 5k+12 \right )=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}(k+2)(5k+19) \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 20.&\textrm{Diketahui bahwa}\: \: S(n)\: \: \textrm{adalah formula dari}\\ &4+5+6+7+...+(n+3)<5n^{2}\\ &\textrm{Jika}\: \: S(n)\: \: \textrm{benar, untuk}\: \: n=k+1,\: \: \textrm{maka}\\ &\textrm{pernyataan ini dapat ditulis dengan}\: ....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&4+5+6+...+(k+4)<5k^{2}\\ \textrm{b}.&4+5+6+...+(k+3)<5k^{2}\\ \textrm{c}.&4+5+6+...+(k+3)<5(k+1)^{2}\\ \color{red}\textrm{d}.&4+5+6+...+(k+4)<5(k^{2}+2k+1)\\ \textrm{e}.&4+5+6+...+(k+4)<5(k+1)(k-1) \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{d}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}&4+5+6+...+(n+3)<5n^{2}\\ &\textrm{Saat}\: \: n=k+1,\: \: \textrm{maka}\\ &4+5+6+...+((k+1)+3)<5(k+1)^{2}\\ &=4+5+6+...+(k+4)<5\left ( k^{2}+2k+1 \right ) \end{aligned} \end{array}$
Contoh Soal 3 Induksi Matematika (Matematika Wajib Kelas XI)
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 11.&\textrm{Perhatikanlah pernyataan-pernyataan berikut}\\ &(1)\quad \displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{5}(5i+2)=4\displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{5}i+10\\ &(2)\quad \displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{5}(5i^{2}-i)=5\displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{5}i^{2}-\sum_{i=1}^{5}i\\ &(3)\quad \displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{5}(3i-4)=3\displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{5}i^{2}-4\\ &(4)\quad \displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{5}(i+7i^{2})=\displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{5}i-7\sum_{i=1}^{5}i\\ &\textrm{Pernyataan yang tepat ditunjukkan oleh}....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \color{red}\textrm{a}.&(1)\: \: \textrm{dan}\: \: (2)\\ \textrm{b}.&(1)\: \: \textrm{dan}\: \: (3)\\ \textrm{c}.&(1)\: \: \textrm{dan}\: \: (4)\\ \textrm{d}.&(2)\: \: \textrm{dan}\: \: (3)\\ \textrm{e}.&(2)\: \: \textrm{dan}\: \: (4) \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{a}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}(1)\quad&\displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{5}(5i+2)=4\displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{5}i+\sum_{i=1}^{5}2\\ &=4\displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{5}i+5\times 2\\ &=4\displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{5}i+10\\ (2)\quad&\displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{5}(5i^{2}-i)=5\displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{5}i^{2}-\sum_{i=1}^{5}i\\ (3)\quad&\displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{5}(3i-4)=3\displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{5}i^{2}-\sum_{i=1}^{5}4\\ &=3\displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{5}i^{2}-5\times 4\\ &=3\displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{5}i^{2}-20\\ (4)\quad&\displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{5}(i+7i^{2})=\displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{5}i+7\sum_{i=1}^{5}i \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 12.&\textrm{Hasil dari}\: \: \displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{4}i^{2}+\sum_{i=5}^{6}i^{2}\\ &\textrm{adalah}\: ....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&\displaystyle 86\\ \color{red}\textrm{b}.&\displaystyle 91\\ \textrm{c}.&\displaystyle 95\\ \textrm{d}.&\displaystyle 101\\ \textrm{e}.&\displaystyle 105 \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{b}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}\displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{4}i^{2}+\sum_{i=5}^{6}i^{2}&=\displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{6}i^{2}\\ &=1^{2}+2^{2}+3^{2}+4^{2}+5^{2}+6^{2}\\ &=1+4+9+16+25+36\\ &=91 \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 13.&\textrm{Hasil dari}\: \: \displaystyle \sum_{i=2}^{5}\left ( 4i^{2}-2i \right )\: \: \textrm{adalah}\: ....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&\displaystyle 144\\ \textrm{b}.&\displaystyle 148\\ \textrm{c}.&\displaystyle 154\\ \textrm{d}.&\displaystyle 164\\ \color{red}\textrm{e}.&\displaystyle 188 \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{e}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}&\displaystyle \sum_{i=2}^{5}\left ( 4i^{2}-2i \right )\\ &=\left ( 4.2^{2}-2.2 \right )+\left ( 4.3^{2}-2.3 \right )+\left ( 4.4^{2}-2.4 \right )+\left ( 4.5^{2}-2.5 \right )\\ &=12+30+56+90\\ &=188 \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 14.&\textrm{Bentuk}\: \: 11^{n}-1\: \: \textrm{dengan}\: \: n\: \: \textrm{bilangan asli}\\ &\textrm{akan habis dibagi oleh}\: ....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&\displaystyle 7\\ \textrm{b}.&\displaystyle 9\\ \color{red}\textrm{c}.&\displaystyle 10\\ \textrm{d}.&\displaystyle 11\\ \textrm{e}.&\displaystyle 13 \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{c}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}\textrm{Bentuk}&\: \: 11^{n}-1\\ \textrm{untuk}&\: \: n=1\\ &=11^{1}-1\\ &=10 \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 15.&\textrm{Rumus yang tepat untuk pola}\: \: 12,13,14,15,...\\ &\textrm{adalah}\: ....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&\displaystyle U_{n}=n+9\\ \textrm{b}.&\displaystyle U_{n}=n+10\\ \color{red}\textrm{c}.&\displaystyle U_{n}=n+11\\ \textrm{d}.&\displaystyle U_{n}=2n+10\\ \textrm{e}.&\displaystyle U_{n}=2n+11 \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{c}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}\textrm{Bentuk}&\: \: 12,13,14,15,...\\ \textrm{untuk}&\: \: U_{n}=pn+q\\ 12&=p+q\\ 13&=2p+q\\ \textrm{akan}&\: \textrm{didapatkan}\\ &\begin{cases} p & =1 \\ q & =11 \end{cases}\\ \textrm{Sehing}&\textrm{ga}\\ U_{n}&=n+11 \end{aligned} \end{array}$
Contoh Soal 2 Induksi Matematika (Matematika Wajib Kelas XI)
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 6.&\textrm{Dengan Induksi Matematika untuk}\: \: n\in \mathbb{N}\\ &\textrm{dapat dibuktikan juga bahwa}\: \: 7^{n}-2^{n}\\ &\textrm{akan habis dibagi oleh}\\ &\begin{array}{lllllll}\\ \textrm{a}.&2\\ \textrm{b}.&3\\ \textrm{c}.&4\\ \color{red}\textrm{d}.&5\\ \textrm{e}.&6\\ \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{d}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}P(n)&=7^{n}-2^{n}\\ P(1)&=7^{1}-2^{1}\\ &=7-2=5\\ &\textrm{adalah bilangan yang habis dibagi 5} \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 7.&\textrm{Diketahui bahwa}\: \: P(n)\: \: \textrm{rumus dari}\\ & 3+6+9+\cdots +3n=\displaystyle \frac{3}{2}n(n+1)\\ &\textrm{maka langkah pertama dengan induksi matematika}\\ &\textrm{dalam pembuktian rumus tersebut adalah}....\\ &\begin{array}{lll}\\ \textrm{a}.&P(n)\: \: \textrm{benar untuk}\: \: n=-1\\ \color{red}\textrm{b}.&P(n)\: \: \textrm{benar untuk}\: \: n=1\\ \textrm{c}.&P(n)\: \: \textrm{benar untuk}\: \: n\: \: \textrm{bilangan bulat}\\ \textrm{d}.&P(n)\: \: \textrm{benar untuk}\: \: n\: \: \textrm{bilangan rasional}\\ \textrm{d}.&P(n)\: \: \textrm{benar untuk}\: \: n\: \: \textrm{bilangan real} \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{b}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}\textrm{Langkah}&\: \textrm{awal yang harus ditunjukkan adalah}\\ n=1&\: \: \textrm{atau}\: \: P(1)\: \: \textrm{harus benar, yaitu}:\\ P(1)&=3.1(\textit{ruas kiri})=\displaystyle \frac{3}{2}.1.(1+1)(\textit{ruas kanan})=3 \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 8.&\textrm{Bila kita hendak membuktikan}\: \: \displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{n}=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}n(n+1)\\ &\textrm{dengan induksi matematika}\\ &\textrm{maka untuk langkah}\: \: n=k+1\\ &\textrm{bentuk yang harus ditunjukkan adalah}...\\ &\begin{array}{lll}\\ \textrm{a}.&1+2+3+\cdots +n=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}n(n+1)\\ \textrm{b}.&1+2+3+\cdots +k=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}k(k+1)\\ \textrm{c}.&1+2+3+\cdots +k=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}k(k+2)\\ \color{red}\textrm{d}.&1+2+3+\cdots +k+(k+1)=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}(k+1)(k+2)\\ \textrm{e}.&1+2+3+\cdots +k+(k+1)=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}(k+2)(k+3)\\ \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{d}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}P(n)&=1+2+3+\cdots +n=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}n(n+1)\\ P(k)&=1+2+3+\cdots +k=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}k(k+1)\\ P(k+1)&=1+2+3+\cdots +k+(k+1)\\ &=\underset{\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}k(k+1)}{\underbrace{1+2+3+\cdots +k}}+(k+1)\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}k(k+1)+(k+1)=(k+1)\left ( \displaystyle \frac{1}{2}k+1 \right )\\ &=(k+1)\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}(k+2)\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}(k+1)(k+2) \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 9.&\textrm{Jika}\: \: P(n)=\displaystyle \frac{n-1}{n+3},\: \textrm{maka}\: \: P(k+1)\\ & \textrm{dinyatakan dengan}\: ....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&\displaystyle \frac{k-1}{k+3}\\ \textrm{b}.&\displaystyle \frac{k-1}{k+4}\\ \color{red}\textrm{c}.&\displaystyle \frac{k}{k+4}\\ \textrm{d}.&\displaystyle \frac{k+1}{k+4}\\ \textrm{e}.&\displaystyle \frac{k+1}{k+5} \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{c}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}P(n)=&\displaystyle \frac{n-1}{n+3}\\ P(k+1)&=\displaystyle \frac{k+1-1}{k+1+3}\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{k}{k+4} \end{aligned}\end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 10.&\textrm{Jika}\: \: P(n)=\displaystyle \frac{n^{2}+1}{4},\: \: \textrm{maka}\\ &\textrm{pernyataan untuk}\: \: P(k+1)\: \: \textrm{adalah}\: ....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&\displaystyle \frac{k^{2}+2k+1}{4}\\ \color{red}\textrm{b}.&\displaystyle \frac{k^{2}+2k+2}{4}\\ \textrm{c}.&\displaystyle \frac{k^{2}+2k+2}{5}\\ \textrm{d}.&\displaystyle \frac{k^{2}+2k+3}{5}\\ \textrm{e}.&\displaystyle \frac{k^{2}+2k+3}{4} \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{b}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}P(n)&=\displaystyle \frac{n^{2}+1}{4}\\ P(k+1)&=\displaystyle \frac{(k+1)^{2}+1}{4}\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{k^{2}+2k+2}{4} \end{aligned} \end{array}$
Contoh Soal 1 Induksi Matematika (Matematika Wajib Kelas XI)
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 1.&\textrm{Hasil dari}\: \: \displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{6}16i\: \: \textrm{adalah}....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&306\\ \textrm{b}.&314\\ \textrm{c}.&326\\ \color{red}\textrm{d}.&336\\ \textrm{e}.&402 \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{d}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}\displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{6}16i&=16.1+16.2+16.3+16.4+16.5+16.6\\ &=16+32+48+64+80+96\\ &=336 \end{aligned}\end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 2.&\textrm{Hasil dari}\: \: \displaystyle \sum_{i=2}^{9}i^{2}\: \: \textrm{adalah}....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&274\\ \textrm{b}.&278\\ \textrm{c}.&280\\ \color{red}\textrm{d}.&284\\ \textrm{e}.&286 \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{d}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}\displaystyle \sum_{i=2}^{9}i^{2}&=2^{2}+3^{2}+4^{2}+5^{2}+..+9^{2}\\ &=4+9+16+25+...+81\\ &=284 \end{aligned}\end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 3.&\textrm{Poa bilangan}\: \: 12,14,16,18,20,...,(2n+10).\\ &\textrm{Nilai suku ke-100 adalah}....\\ &\begin{array}{lll}\\ \textrm{a}.&180\\ \textrm{b}.&194\\ \textrm{c}.&198\\ \textrm{d}.&208\\ \color{red}\textrm{e}.&210\\ \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{e}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}U_{n}&=2n+10\\ U_{100}&=2\times 100+10\\ &=210 \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 4.&\textrm{Diketahui bahwa jika}\\ & 31+39+47+\cdots +8n+23=4n^{2}+27n\\ & \textrm{dengan}\: \: k,n\in \mathbb{N}\: \: \textrm{maka}\\ & 31+39+47+\cdots +8n+23+8k+31=....\\ &\begin{array}{lllllll}\\ \textrm{a}.&4k^{2}+27k\\ \textrm{b}.&4k^{2}+35k\\ \color{red}\textrm{c}.&4k^{2}+35k+31\\ \textrm{d}.&4k^{2}+35k+1\\ \textrm{e}.&4k^{2}+35k+54\\ \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{c}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}&\underset{4k^{2}+27k}{\underbrace{31+39+47+\cdots +8k+23}}+8k+31\\ &=4k^{2}+27k+8k+31\\ &=4k^{2}+35k+31 \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 5.&\textrm{Dengan Induksi Matematika untuk}\: \: n\in \mathbb{N}\\ &\textrm{dapat dibuktikan bahwa}\: \: n(n+1)(n+2)\\ &\textrm{akan habis dibagi oleh}\\ &\begin{array}{lllllll}\\ \textrm{a}.&4\\ \textrm{b}.&5\\ \color{red}\textrm{c}.&6\\ \textrm{d}.&7\\ \textrm{e}.&8\\ \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{c}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}P(n)&=n(n+1)(n+2)\\ P(1)&=1(1+1)(1+2)=1.2.3\\ &\textrm{adalah bilangan yang habis dibagi 6} \end{aligned} \end{array}$
Contoh Soal 6 Persamaan Trigonometri (Matematika Peminatan Kelas XI)
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 26.&\textrm{Jika nilai}\: \: \cot A+\cos A=x\\ &\textrm{dan}\: \: \cot A-\cos A=y,\\ &\textrm{maka nilai}\: \: \left ( x^{2}-y^{2} \right )=\: ....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \color{red}\textrm{a}.&4\sqrt{xy}\\ \textrm{b}.&2\sqrt{xy}\\ \textrm{c}.&xy\\ \textrm{d}.&2\\ \textrm{e}.&4 \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{a}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}\color{magenta}xy&=\left (\cot A+\cos A \right )\left ( \cot A-\cos A \right )\\ &=\cot ^{2}A-\cos ^{2}A\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{\cos^{2}A }{\sin ^{2}A}-\cos ^{2}A\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{\cos^{2}A }{\sin ^{2}A}-\cos ^{2}A\times \frac{\sin ^{2}A}{\sin ^{2}A}\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{\cos ^{2}A}{\sin ^{2}A}\left ( 1-\sin ^{2}A \right )\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{\cos ^{4}A}{\sin ^{2}A}\\ \sqrt{xy}&=\displaystyle \frac{\cos A}{\sin A}\times \cos A\\ \color{black}\textrm{Se}&\color{black}\textrm{lanjutnya}\\ x^{2}-y^{2}&=\left (\cot A+\cos A \right )^{2}-\left ( \cot A-\cos A \right )^{2}\\ (x+y)&(x-y)=(\cot A+\cos A+\cot A-\cos A)\\ &\qquad\times (\cot A+\cos A-(\cot A-\cos A))\\ x^{2}-y^{2}&=2\cot A\times 2\cos A\\ &=4\times \displaystyle \frac{\cos A}{\sin A}\times \cos A\\ &=\color{magenta}4\sqrt{xy} \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 27.&\textrm{Jika nilai}\: \: \cos A+\sin A=\sqrt{2}\cos A\\ &\textrm{maka nilai}\: \: \left ( \cos A-\sin A \right )=\: ....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&-\sqrt{2}\cos A\\ \textrm{b}.&-\sqrt{2}\sin A\\ \color{red}\textrm{c}.&\sqrt{2}\sin A\\ \textrm{d}.&\displaystyle \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\sec A\\ \textrm{e}.&\displaystyle \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\csc A \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{c}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}\cos A+\sin A&=\sqrt{2}\cos A\\ \left (\cos A+\sin A \right )^{2}&=\left (\sqrt{2}\cos A \right )^{2}\\ 1+2\sin A\cos A&=2\cos ^{2}A\\ 2\sin A\cos A&=2\cos ^{2}A-1\\ \textrm{maka}&\\ \left (\cos A-\sin A \right )^{2}&=1-2\sin A\cos A\\ &=1-\left ( 2\cos ^{2}A-1 \right )\\ &=2-2\cos ^{2}A\\ &=2\left ( 1-\cos ^{2}A \right )\\ &=2\sin ^{2}A\\ \cos A-\sin A&=\sqrt{2\sin ^{2}A}\\ &=\sin A\sqrt{2}\\ &=\color{magenta}\sqrt{2}.\sin A \end{aligned} \end{array}$
DAFTAR PUSTAKA
- Sembiring, S., Zulkifli, M., Marsito, dan Rusdi, I. 2017. Matematika untuk Siswa SMA/MA Kelas XI Kelompok Peminatan Matematika dan Ilmu-Ilmu Alam. Bandung: SEWU.
- Sukino. 2016. Matematika untuk SMA/MA Kelas XI Kelompok Peminatan Matematika dan Ilmu-Ilmu Alam. Jakarta: ERLANGGA
Contoh Soal 5 Persamaan Trigonometri (Matematika Peminatan Kelas XI)
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 21.&\textrm{Nilai dari}\: \: \displaystyle \frac{1}{\sec ^{2}A}+\frac{1}{\csc ^{2}A}=....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&-\infty \\ \textrm{b}.&\displaystyle -1\\ \textrm{c}.&\displaystyle 0\\ \color{red}\textrm{d}.&\displaystyle 1\\ {e}.&\displaystyle \infty \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{d}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}&\displaystyle \frac{1}{\sec ^{2}A}+\frac{1}{\csc ^{2}A}\\ &=\cos ^{2}A+\sin ^{2}=1 \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 22.&\textrm{Nilai dari}\: \: \displaystyle \frac{\tan B+\tan C}{\cot B+\cot C}=....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&\cot B\times \cot C \\ \color{red}\textrm{b}.&\displaystyle \tan B\times \tan C\\ \textrm{c}.&\displaystyle \sec B\times \csc C\\ \textrm{d}.&\displaystyle \tan B\times \cot C\\ {e}.&\displaystyle \tan B\times \csc C \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{b}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}&\displaystyle \frac{\tan B+\tan C}{\cot B+\cot C}\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{\tan B+\tan C}{\displaystyle \frac{1}{\tan B}+\frac{1}{\tan C}}\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{\tan B+\tan C}{\left ( \displaystyle \frac{\tan B+\tan C}{\tan B\times \tan C} \right )}\\ &=\tan B\times \tan C \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 23.&\textrm{Nilai dari}\\ &\displaystyle \frac{\tan A}{\sec A-1}+\frac{\tan A}{\sec A+1}=....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&2\tan A \\ \textrm{b}.&2\cot A\\ \textrm{c}.&\displaystyle 2\sec A\\ \color{red}\textrm{d}.&\displaystyle 2\csc A\\ {e}.&\displaystyle 2\tan A.\sec A \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{d}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}&\displaystyle \frac{\tan A}{\sec A-1}+\frac{\tan A}{\sec A+1}\\ &=\tan A\left (\displaystyle \frac{1}{\displaystyle \frac{1}{\cos A}-1}+\frac{1}{\displaystyle \frac{1}{\cos A}+1} \right )\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{\sin A}{\cos A}\left ( \displaystyle \frac{\cos A}{1-\cos A}+\frac{\cos A}{1+\cos A} \right )\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{\sin A}{1-\cos A}+\frac{\sin A}{1+\cos A}\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{\sin A(1+\cos A)+\sin A(1-\cos A)}{(1-\cos A)(1+\cos A)}\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{2\sin A}{1-\cos ^{2}}\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{2\sin A}{\sin ^{2}A}\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{2}{\sin A}\\ &=2\csc A \end{aligned}\\\\ &\textrm{Sebagai catatanya}\\ &\textrm{Anda bisa gunakan cara yang lain} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 24.&\textrm{Nilai}\: \: x\: \: \textrm{yang memenuhi persamaan}\\ &\sin \left ( 2x-20^{\circ} \right )=-\cos \left ( 3x+50^{\circ} \right )\\ &\textrm{adalah}\: ....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&-30^{\circ}\\ \textrm{b}.&-25^{\circ}\\ \color{red}\textrm{c}.&20^{\circ}\\ \textrm{d}.&25^{\circ}\\ {e}.&30^{\circ} \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{c}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}\sin \left ( 2x-20^{\circ} \right )&=-\cos \left ( 3x+50^{\circ} \right )\\ \sin \left ( 20^{\circ}-2x \right )&=\cos \left ( 3x+50^{\circ} \right )\\ \sin A&=\cos B,\: \: \color{black}\textrm{artinya}\\ A+B&=90^{\circ},\: \: \color{magenta}\textrm{maka}\\ \left ( 20^{\circ}-2x \right )+\left ( 3x+50^{\circ} \right )&=90^{\circ}\\ x+70^{\circ}&=90^{\circ}\\ x&=90^{\circ}-70^{\circ}\\ &=20^{\circ} \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 25.&\textrm{Nilai}\: \: x\: \: \textrm{yang memenuhi persamaan}\\ &\tan \left ( 2x+60^{\circ} \right )=\cot \left ( 90^{\circ}-3x \right )\\ &\textrm{adalah}\: ....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&20^{\circ}\\ \textrm{b}.&30^{\circ}\\ \textrm{c}.&40^{\circ}\\ \textrm{d}.&50^{\circ}\\ \color{red}\textrm{e}.&60^{\circ} \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{e}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}\tan \left ( 2x+60^{\circ} \right )&=\cot \left ( 90^{\circ}-3x \right )\\ \tan (2x+60^{\circ})&=\tan 3x\\ 2x+60^{\circ}&=3x\\ 2x-3x&=-60^{\circ}\\ -x&=-60^{\circ}\\ x&=60^{\circ} \end{aligned} \end{array}$
Contoh Soal 4 Persamaan Trigonometri (Matematika Peminatan Kelas XI)
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 16.&\textrm{Jika}\: \: \tan^{2} x +\sec x =5 \: \: \textrm{untuk}\\ &0\leq x\leq \displaystyle \frac{\pi }{2}\: \: \textrm{maka nilai} \: \: \cos x=....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&0\\ \color{red}\textrm{b}.&\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}\\ \textrm{c}.&\displaystyle \frac{1}{3}\\ \textrm{d}.&\displaystyle \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\\ \textrm{e}.&\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}\sqrt{3} \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{b}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}\textrm{Ingat bahwa}&\: \: 0\leq x\leq \displaystyle \frac{\pi }{2}\\ \textrm{berarti sudu}&\textrm{t}\: \: x\: \: \textrm{berada di kuadran I}\\ \textrm{sehingga ak}&\textrm{an menyebabkan nilai}\\ & \color{magenta}\cos x=+\\ \color{black}\textrm{Selanjutnya}&\\ \tan^{2} x +\sec x &=5\\ \sec ^{2}x-1+\sec x&=5\\ \sec ^{2}x+\sec x-6&=0\\ (\sec x+3)(\sec x-2)&=0\\ \sec x=-3\: \: \textrm{atau}&\sec x=2\\ \textrm{untuk}\: \: \sec x&=-3\: \: (\color{red}\textrm{tidak memenuhi})\\ \textrm{untuk}\: \: \sec x&=2\: \: (\color{magenta}\textrm{memenuhi})\\ \color{black}\textrm{Selanjutnya}&\: \color{black}\textrm{lagi}\\ \sec x&=2\\ \displaystyle \frac{1}{\cos x}&=2\\ \cos x&=\color{magenta}\displaystyle \frac{1}{2} \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 17.&\textrm{Nilai}\\ &\left ( \sin A+\cos A \right )^{2}+\left ( \sin A-\cos A \right )^{2}=....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&1\\ \color{red}\textrm{b}.&\displaystyle 2\\ \textrm{c}.&\displaystyle 3\\ \textrm{d}.&\displaystyle 3\cos A\\ {e}.&\displaystyle 4\sin A \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{b}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}&\left ( \sin A+\cos A \right )^{2}+\left ( \sin A-\cos A \right )^{2}\\ &=\sin ^{2}A+2\sin A\cos A+\cos ^{2}A\\ &\quad +\sin ^{2}A-2\sin A\cos A+\cos ^{2}A\\ &=1+1\\ &=2 \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 18.&\textrm{Nilai}\: \: \sqrt{\displaystyle \frac{1+\sin A}{1-\sin A}}=....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \color{red}\textrm{a}.&\sec A+\tan A\\ \textrm{b}.&\sec ^{2}A+\tan ^{2}A\\ \textrm{c}.&\sec ^{2}A-\tan ^{2}A\\ \textrm{d}.&\tan ^{2}A-\sec ^{2}A\\ {e}.&\sec A\times \tan A \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{a}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}&\sqrt{\displaystyle \frac{1+\sin A}{1-\sin A}}\\ &=\sqrt{\displaystyle \frac{1+\sin A}{1-\sin A}\times \frac{1+\sin A}{1+\sin A}}\\ &=\sqrt{\displaystyle \frac{\left ( 1+\sin A \right )^{2}}{1-\sin ^{2}A}}\\ &=\sqrt{\displaystyle \frac{\left ( 1+\sin A \right )^{2}}{\cos ^{2}A}}\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{1+\sin A}{\cos A}\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{1}{\cos A}+\frac{\sin A}{\cos A}\\ &=\sec A+\tan A \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 19.&\textrm{Jika}\: \: 0^{\circ}\leq \theta \leqslant 90^{\circ},\: \textrm{maka nilai}\\ &\left ( \displaystyle \frac{5\cos \theta -4}{3-5\sin \theta }-\frac{3+5\sin \theta }{4+5\cos \theta } \right )=....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&-1\\ \color{red}\textrm{b}.&\displaystyle 0\\ \textrm{c}.&\displaystyle \frac{1}{4}\\ \textrm{d}.&\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}\\ {e}.&\displaystyle 1 \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{b}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}&\left ( \displaystyle \frac{5\cos \theta -4}{3-5\sin \theta }-\frac{3+5\sin \theta }{4+5\cos \theta } \right )\\ &=\left ( \displaystyle \frac{5\cos \theta -4}{3-5\sin \theta }\times \frac{4+5\cos \theta }{4+5\cos \theta } \right )\\ &\qquad-\left ( \displaystyle \frac{3+5\sin \theta }{4+5\cos \theta }\times \frac{3-5\sin \theta }{3-5\sin \theta } \right )\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{25\cos ^{2}-16-\left ( 9-25\sin ^{2}\theta \right )}{(3-5\sin \theta )(4+5\cos \theta )}\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{25\left ( \sin ^{2}\theta +\cos ^{2}\theta \right )-25}{(3-5\sin \theta )(4+5\cos \theta )}\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{0}{(3-5\sin \theta )(4+5\cos \theta )}\\ &=\color{magenta}0 \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 20.&\textrm{Nilai}\\ &\left ( 1+\cot \theta -\csc \theta \right )\left ( 1+\tan \theta +\sec \theta \right )=....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&-2\\ \textrm{b}.&\displaystyle -1\\ \textrm{c}.&\displaystyle 0\\ \textrm{d}.&\displaystyle 1\\ \color{red}\textrm{e}.&\displaystyle 2 \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{e}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}&\left ( 1+\cot \theta -\csc \theta \right )\left ( 1+\tan \theta +\sec \theta \right )\\ &=\left ( 1+\displaystyle \frac{\cos \theta }{\sin \theta } -\frac{1}{\sin \theta } \right )\left ( 1+\frac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta } +\frac{1}{\cos \theta } \right )\\ &=\left ( \displaystyle \frac{\sin \theta +\cos \theta -1}{\sin \theta } \right )\left ( \displaystyle \frac{\cos \theta +\sin \theta +1}{\cos \theta } \right )\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{\left (\sin \theta +\cos \theta \right )^{2}-1}{\sin \theta \cos \theta }\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{1+2\sin \theta \cos \theta -1}{\sin \theta \cos \theta }\\ &=2 \end{aligned} \end{array}$
Contoh Soal 3 Persamaan Trigonometri (Matematika Peminatan Kelas XI)
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 11.&\textrm{Himpunan penyelesaian persamaan}\\ &3\cos 2x+5\sin x+1=0\: \: \textrm{untuk}\: \: 0^{\circ}\leq x\leq 2\pi \\ &\textrm{adalah}\: ....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \color{red}\textrm{a}.&\left \{ \displaystyle \frac{7}{6}\pi ,\frac{11}{6}\pi \right \}\\ \textrm{b}.&\left \{ \displaystyle \frac{5}{6}\pi ,\frac{11}{6}\pi \right \}\\ \textrm{c}.&\left \{ \displaystyle \frac{1}{6}\pi ,\frac{7}{6}\pi \right \}\\ \textrm{d}.&\left \{ \displaystyle \frac{1}{5}\pi ,\frac{5}{6}\pi \right \}\\ \textrm{e}.&\left \{ \displaystyle \frac{5}{6}\pi ,\frac{7}{6}\pi \right \} \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{a}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}3\cos 2x+5\sin x+1&=0\\ 3\left ( 1-2\sin ^{2}x \right )+5\sin x+1&=0\\ -6\sin ^{2}+5\sin x+4&=0\\ 6\sin ^{2}x-5\sin x-4&=0\\ \left ( 3\sin x-4 \right )\left ( 2\sin x+1 \right )&=0\\ \sin x=\displaystyle \frac{4}{3}\: \: \textrm{atau}\: \: \sin x&=-\frac{1}{2}\\ \sin x&=\sin 150^{\circ}=\frac{5}{6}\pi \\ x&=\begin{cases} \displaystyle \frac{7}{6}\pi &+k.2\pi \\ \pi -\displaystyle \frac{7}{6}\pi & +k.2\pi \end{cases}\\ \textrm{saat}\: \: k&=0\\ x_{1}&=\displaystyle \frac{7}{6}\pi \\ x_{2}&=-\displaystyle \frac{1}{6}\pi \\ \textrm{saat}\: \: k&=1\\ x_{1}&=\color{red}\displaystyle \frac{7}{6}\pi +2\pi \\ x_{2}&=-\displaystyle \frac{1}{6}\pi +2\pi =\frac{11}{6}\pi \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 12.&\textrm{Himpunan penyelesaian dari}\\ &\sqrt{3}\sin 2x+2\cos ^{2}x=-1\: \: \textrm{untuk}\\ &0^{\circ}\leq x\leq 360^{\circ}\: \: \textrm{adalah}\: ....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&\left \{ 240^{\circ},300^{\circ} \right \}\\ \textrm{b}.&\left \{ 30^{\circ},60^{\circ} \right \}\\ \textrm{c}.&\left \{ 150^{\circ},315^{\circ} \right \}\\ \color{red}\textrm{d}.&\left \{ 120^{\circ},300^{\circ} \right \}\\ \textrm{e}.&\left \{ 60^{\circ},150^{\circ} \right \} \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{d}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}\sqrt{3}\sin 2x+2\cos ^{2}x&=-1\\ \sqrt{3}\sin 2x+1+\cos 2x&=-1\\ \sqrt{3}\sin 2x+\cos 2x&=-2\\ \sqrt{\sqrt{3}^{2}+1^{2}}\cos \left ( 2x-\alpha \right )&=-2\\ a=x=1,\: \: b&=y=\sqrt{3}\\ \alpha &=\arctan \displaystyle \frac{b}{a}=\arctan \frac{\sqrt{3}}{1}\\ \alpha &=60^{\circ}\\ \textrm{maka persamaan akan}&\: \textrm{menjadi}\\ 2\cos \left ( 2x-60^{\circ} \right )&=-2\\ \cos \left ( 2x-60^{\circ} \right )&=-1\\ \cos \left ( 2x-60^{\circ} \right )&=\cos 180^{\circ}\\ \left ( 2x-60^{\circ} \right )&=\pm 180^{\circ}+k.360^{\circ}\\ 2x&=60^{\circ}\pm 180^{\circ}+k.360^{\circ}\\ x&=30^{\circ}\pm 90^{\circ}+k.180^{\circ}\\ \textrm{saat}\: \: k&=0\\ x_{1}&=120^{\circ}\\ x_{2}&=-60^{\circ}\\ \textrm{saat}\: \: k&=1\\ x_{3}&=120^{\circ}+360^{\circ}=....\\ x_{2}&=-60^{\circ}+360^{\circ}=300^{\circ} \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 13.&\textrm{Jika}\: \: 3\sin \theta +4\cos \theta =5 \: \: \textrm{maka}\\ &\textrm{nilai dari} \: \: \sin \theta \: \: \textrm{adalah}\: ....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&0,3\\ \color{red}\textrm{b}.&0,60\\ \textrm{c}.&0,75\\ \textrm{d}.&0,80\\ \textrm{e}.&1,20 \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{b}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}3\sin \theta +4\cos \theta &=5\\ k\cos \left ( \theta -\alpha \right )&=5\\ a=x=4,\: &b=y=3\\ \theta &=\arctan \displaystyle \frac{b}{a}\\ \theta &=\arctan \displaystyle \frac{3}{4}\\ \color{black}\textrm{atau}\: \: &\\ \tan \theta &=\displaystyle \frac{3}{4}\\ \color{black}\textrm{maka}\: \: &\\ \sin \theta &=\displaystyle \frac{3}{\sqrt{3^{2}+4^{2}}}\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{3}{5}\\ &=\color{magenta}0,6 \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 14.&\textrm{Jika}\: \: \tan \theta +\sec \theta =x \: \: \textrm{maka}\\ &\textrm{nilai dari} \: \: \tan \theta \: \: \textrm{adalah}\: ....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&\displaystyle \frac{2x}{x^{2}-1}\\ \textrm{b}.&\displaystyle \frac{2x}{x^{2}+1}\\ \textrm{c}.&\displaystyle \frac{x^{2}+1}{2x}\\ \color{red}\textrm{d}.&\displaystyle \frac{x^{2}-1}{2x}\\ \textrm{e}.&\displaystyle \frac{x^{2}-1}{x^{2}+1} \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{d}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}\color{black}\textrm{Langkah}&\: \: 1\\ \tan \theta +\sec \theta &=x\\ \displaystyle \frac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta } +\frac{1}{\cos \theta }&=x\\ \displaystyle \frac{\sin \theta +1}{\cos \theta }&=x\\ \sin \theta +1&=x\cos \theta ...........1\\ \color{black}\textrm{Langkah}&\: \: 2\\ \left (\tan \theta +\sec \theta \right )^{2}&=x^{2}\\ \tan ^{2}\theta +2\tan \theta \sec \theta +\sec ^{2}\theta &=x^{2}\\ \sec ^{2}\theta -1+2\tan \theta \sec \theta &+\sec ^{2}\theta =x^{2}\\ 2\sec ^{2}\theta +2\tan \theta \sec \theta &=x^{2}+1\\ \displaystyle \frac{2}{\cos ^{2}\theta }+\frac{2\sin \theta }{\cos ^{2}\theta }&=x^{2}+1\\ 1+\sin \theta &=\left (\displaystyle \frac{x^{2}+1}{2} \right )\cos ^{2}\theta.....2\\ \color{black}\textrm{Langkah}&\: \: 3\\ \left (\displaystyle \frac{x^{2}+1}{2} \right )\cos ^{2}&=x\cos \theta \\ \cos \theta &=\displaystyle \frac{2x}{x^{2}+1}\\ \textrm{maka}\: \: &(\color{magenta}\textbf{dengan sisi segitiga})\\ \tan \theta =\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{\left ( x^{2}+1 \right )^{2}-(2x)^{2}}}{2x}&=\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{x^{4}+2x^{2}+1-4x^{2}}}{2x}\\ \tan \theta &=\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{x^{4}-2x^{2}+1}}{2x}\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{\left ( x^{2}-1 \right )^{2}}}{2x}\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{x^{2}-1}{2x} \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{aligned}.\: \: \qquad \textbf{Sehingga}&\: \textbf{dari kasus di atas didapatkan}\\ \color{magenta}\sin \theta &=\displaystyle \frac{x^{2}-1}{x^{2}+1}\\ \color{magenta}\cos \theta &=\displaystyle \frac{2x}{x^{2}+1}\\ \color{magenta}\tan \theta &=\displaystyle \frac{x^{2}-1}{2x} \end{aligned}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 15.&\textrm{Jika}\: \: \sec x +\tan x =\displaystyle \frac{3}{2} \: \: \textrm{untuk}\\ &0\leq x\leq \displaystyle \frac{\pi }{2}\: \: \textrm{maka nilai} \: \: \sin x=....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \color{red}\textrm{a}.&\displaystyle \frac{5}{13}\\ \textrm{b}.&\displaystyle \frac{12}{13}\\ \textrm{c}.&\displaystyle 1\\ \textrm{d}.&\displaystyle \frac{2}{13}\\ \textrm{e}.&\displaystyle \frac{5}{12} \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{a}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}\sec x +\tan x &=\displaystyle \frac{3}{2}\\ \textrm{ingat saat}&\: \color{black}\textrm{mengerjakan soal no}.14\\ \sec \theta +\tan \theta &=x\\ \sin \theta &=\displaystyle \frac{x^{2}-1}{x^{2}+1},\: \: \color{black}\textrm{maka}\\ \sin x&=\color{magenta}\displaystyle \frac{\left ( \displaystyle \frac{3}{2} \right )^{2}-1}{\left (\displaystyle \frac{3}{2} \right )^{2}+1}\\ &=\displaystyle \frac{\displaystyle \frac{9}{4}-1}{\displaystyle \frac{9}{4}+1}\\ &=\frac{\displaystyle \frac{5}{4}}{\displaystyle \frac{13}{4}}\\ &=\color{magenta}\displaystyle \frac{5}{13} \end{aligned} \end{array}$
Contoh Soal 2 Persamaan Trigonometri (Matematika Peminatan Kelas XI)
Contoh Soal 1 Persamaan Trigonometri (Matematika Peminatan Kelas XI)
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 1.&\textrm{Himpunan penyelesaian dari}\\ &\sin 2x=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}\sqrt{3}\: \: \textrm{untuk}\: \: 0^{\circ}\leq x\leq 360^{\circ}\\ &\textrm{adalah}\: ....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&\left \{ 30^{\circ},210^{\circ} \right \}\\ \textrm{b}.&\left \{ 60^{\circ},240^{\circ} \right \}\\ \textrm{c}.&\left \{ 30^{\circ},60^{\circ},210^{\circ} \right \}\\ \color{red}\textrm{d}.&\left \{ 30^{\circ},60^{\circ},210^{\circ},240^{\circ} \right \}\\ \textrm{e}.&\left \{ 30^{\circ},60^{\circ},210^{\circ},240^{\circ},270^{\circ} \right \} \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{d}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}\sin 2x&=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}\sqrt{3}\\ \sin 2x&=\sin 60^{\circ}\\ 2x&=\begin{cases} 60^{\circ} & +k.360^{\circ} \\ \left ( 180^{\circ}-60^{\circ} \right ) & +k.360^{\circ} \end{cases}\\ x&=\begin{cases} 30^{\circ} & +k.180^{\circ}\\ 60^{\circ} & +k.180^{\circ} \end{cases}\\ \textrm{saat}&\: \: k=0\\ x&=\begin{cases} 30^{\circ} & \\ 60^{\circ} & \end{cases}\\ \textrm{saat}&\: \: k=1\\ x&=\begin{cases} 30^{\circ} & +1.180^{\circ}=210^{\circ}\\ 60^{\circ} & +1.180^{\circ}=240^{\circ} \end{cases}\\ \textrm{saat}&\: \: k=2\\ x&=\begin{cases} 30^{\circ} & +2.180^{\circ}=\color{red}390^{\circ}\\ 60^{\circ} & +2.180^{\circ}=\color{red}420^{\circ} \end{cases}\\ \color{red}\textrm{kedua}&\color{red}\textrm{nnya tidak memenuhi} \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 2.&\textrm{Himpunan penyelesaian dari}\\ &\tan 2x-\sqrt{3}=0\: \: \textrm{untuk}\: \: 0^{\circ}\leq x\leq 360^{\circ}\\ &\textrm{adalah}\: ....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&\left \{ 15^{\circ},105^{\circ},195^{\circ},285^{\circ} \right \}\\ \color{red}\textrm{b}.&\left \{ 30^{\circ},120^{\circ},210^{\circ},300^{\circ} \right \}\\ \textrm{c}.&\left \{ 45^{\circ},135^{\circ},225^{\circ},315^{\circ} \right \}\\ \textrm{d}.&\left \{ 15^{\circ},105^{\circ},195^{\circ},285^{\circ} \right \}\\ \textrm{e}.&\left \{ 15^{\circ},30^{\circ},45^{\circ},60^{\circ},75^{\circ} \right \} \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{b}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}\tan 2x&-\sqrt{3}=0\\ \tan 2x&=\sqrt{3}\\ \tan 2x&=\tan 60^{\circ}\\ 2x&=60+k.180^{\circ}\\ x&=30^{\circ}+k.90^{\circ}\\ \textrm{saat}&\: \: k=0\\ x&=30^{\circ}\\ \textrm{saat}&\: \: k=1\\ x&=30^{\circ}+90^{\circ}=120^{\circ}\\ \textrm{saat}&\: \: k=2\\ x&=30^{\circ}+180^{\circ}=210^{\circ}\\ \textrm{saat}&\: \: k=3\\ x&=30^{\circ}+270^{\circ}=300^{\circ}\\ \textrm{saat}&\: \: k=4\\ x&=30^{\circ}+360^{\circ}=\color{red}390^{\circ}\\ \color{red}\textrm{tidak}&\: \color{red}\textrm{memenuhi} \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 3.&\textrm{Himpunan penyelesaian dari}\\ &\cos 3x=-\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}\sqrt{3}\: \: \textrm{untuk}\: \: 0^{\circ}\leq x\leq 180^{\circ}\\ &\textrm{adalah}\: ....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \textrm{a}.&\left \{ 40^{\circ},80^{\circ} \right \}\\ \textrm{b}.&\left \{ 50^{\circ},70^{\circ} \right \}\\ \textrm{c}.&\left \{ 40^{\circ},70^{\circ},80^{\circ} \right \}\\ \color{red}\textrm{d}.&\left \{ 50^{\circ},70^{\circ},170^{\circ} \right \}\\ \textrm{e}.&\left \{ 50^{\circ},80^{\circ},170^{\circ} \right \} \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{d}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}\cos 3x&=-\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}\sqrt{3}\\ \cos 3x&=-\cos 30^{\circ}\\ \cos 3x&=\cos \left (180^{\circ}-30^{\circ} \right )=\cos 150^{\circ}\\ 3x&=\pm 150^{\circ}+k.360^{\circ}\\ x&=\pm 50^{\circ}+k.120^{\circ}\\ \textrm{saat}&\: \: k=0\\ x&=\pm 50^{\circ}\: \rightarrow x=50^{\circ}\: \: (\textrm{mm})\\ \textrm{saat}&\: \: k=1\\ x&=\pm 50^{\circ}+120^{\circ}=\begin{cases} 170^{\circ} & (\textrm{mm}) \\ 70^{\circ} & (\textrm{mm}) \end{cases} \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 4.&\textrm{Nilai}\: \: x\: \: \textrm{yang memenuhi persamaan}\\ &2\cos ^{2}x+\cos x-1=0\: \: \textrm{untuk}\: \: 0\leq x\leq \pi \\ &\textrm{adalah}\: ....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \color{red}\textrm{a}.&\displaystyle \frac{1}{3}\pi \: \: \textrm{dan}\: \: \pi \\ \textrm{b}.&\displaystyle \frac{1}{3}\pi \: \: \textrm{dan}\: \: \frac{2}{3}\pi \\ \textrm{c}.&\displaystyle \frac{1}{3}\pi \: \: \textrm{dan}\: \: \frac{3}{4}\pi \\ \textrm{d}.&\displaystyle \frac{1}{4}\pi \: \: \textrm{dan}\: \: \frac{3}{4}\pi \\ \textrm{e}.&\displaystyle \frac{1}{4}\pi \: \: \textrm{dan}\: \: \frac{2}{3}\pi \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{a}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}2\cos ^{2}x+\cos x-1&=0\\ \left (2\cos x-1 \right )\left (\cos x+1 \right )&=0\\ \cos x=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}\: \: \color{magenta}\textrm{atau}\: \: &\cos x=-1\\ \cos x=\cos 60^{\circ}=\cos \frac{1}{3}\pi \: \: &\\ \color{magenta}\textrm{atau}\: \: \cos x&=\cos 180^{\circ}=\cos \pi \\ \end{aligned} \end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}\\ 5.&\textrm{Untuk}\: \: x\: \: \textrm{yang memenuhi persamaan}\\ &\tan ^{2}x-\tan x-6=0\: \: \textrm{pada}\: \: 0\leq x\leq \pi ,\\ &\textrm{maka himpunan nilai}\: \: \sin x\: \: \textrm{adalah}\: ....\\ &\begin{array}{llll}\\ \color{red}\textrm{a}.&\left \{ \displaystyle \frac{3\sqrt{10}}{10},\frac{2\sqrt{5}}{5} \right \}\\ \textrm{b}.&\left \{ \displaystyle \frac{3\sqrt{10}}{10},-\frac{2\sqrt{5}}{5} \right \} \\ \textrm{c}.&\left \{ -\displaystyle \frac{3\sqrt{10}}{10},\frac{2\sqrt{5}}{5} \right \} \\ \textrm{d}.&\left \{ \displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{10}}{10},\frac{\sqrt{5}}{5} \right \} \\ \textrm{e}.&\left \{ \displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{10}}{10},\frac{2\sqrt{5}}{5} \right \} \end{array}\\\\ &\textrm{Jawab}:\quad \color{red}\textbf{a}\\ &\color{blue}\begin{aligned}\tan ^{2}x-\tan x-6&=0\\ \left (\tan x-3 \right )\left (\tan x+2 \right )&=0\\ \tan x=3\: \: \textrm{atau}\: \: &\tan x=-2\\ \tan x=\displaystyle \frac{3}{1}\: \: \textrm{atau}\: \: &\tan x=\frac{-2}{1}\\ \sin x=\displaystyle \frac{3}{\sqrt{1^{2}+3^{2}}}\: \: \textrm{atau}\: \: &\sin x=\frac{2}{\sqrt{1^{2}+2^{2}}}\\ \sin x=\displaystyle \frac{3}{\sqrt{10}}\: \: \textrm{atau}\: \: &\sin x=\frac{2}{\sqrt{5}}\\ \sin x=\displaystyle \frac{3}{10}\sqrt{10}\: \: \textrm{atau}\: \: &\sin x=\frac{2}{5}\sqrt{5} \end{aligned} \end{array}$